Eye Disorders – Information to patients about the most common eye diseases
Alacrimia, Dry Eye Syndrome
After spending a lot of time at the computer, my eyes feel irritated and sandy.
My eyes are tired and irritated. Worst is when I try and read or watch TV.
Symptoms. Dry eye syndrome affects many people. Dry eye syndrome is more common in seniors, but it can also happen to young people. Dry eye is often associated to certain activities such as reading or sitting in front a computer screen. Many people feel dry eyes, fatigue, irritation, or pain. This is because there is no tear film, also known as tears or lacrimal liquid. Without this fluid, it becomes impossible for the eyeball to retain moisture. It can cause minor irritations, skin reddening, and the sensation of foreign bodies.
Treatment. Although Alacrimia can’t be cured completely, there are ways to improve the symptoms.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis, a chronic inflammation of the eyelids and eyelashes, is one of the most common conditions that doctors see in their clinics. Blepharitis is a common condition in both children and adults. It can cause erythema, swelling, itching, and irritation of the eyeslids. Blepharitis is most commonly caused by poor hygiene, excessive oil production from the glands on the eyelids, allergic reactions, and bacterial infections.
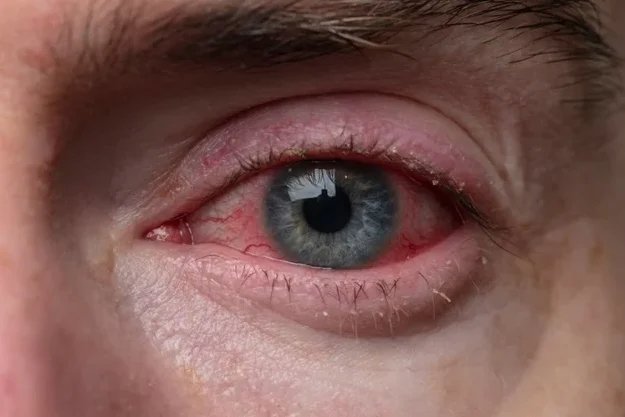
Chalazion
A chalazion refers to a small, firm swelling of the eyelid caused by an infection or blocked opening in the upper or lower eyelids. This condition is often associated with blepharitis. Chalazion cancers can cause discomfort, unsightly, and may obstruct normal sight. Initial symptoms include redness, swelling, and sensitive. Rarely, the Chalazion can grow to the point that it presses on the eyelid, causing blurred vision.
Keratoconus
What is keratoconus, you ask? Keratoconus, which is the medical name for a convex cornea, is a condition that affects one in every ten people. Keratoconus is a condition which usually does not manifest until the end of adolescence. This is a congenital refractive error, which results in corneal growth that is irregular and difficult to correct. The cornea is usually convex with a smooth anterior surface. This allows light to penetrate uniformly to the lens and reach the retina. Keratoconus is when the cornea’s structure becomes weaker, and it begins to thin out, eventually becoming a cone-shaped shape. It is partly hereditary, and occurs more often in boys.
Symptoms. Keratoconus gradually affects the vision. The disease’s progression ceases at 40. The changes that do occur after that point are usually mild and gradual. The vision can become blurred over time and there may be lesions or transient pain. In rare cases, an increase in inflammation of the cornea could cause temporary blindness. Hydropic attack is a sudden inflammation. The treatment involves applying an antibacterial and lubricating ointment. Although it can be considered serious, it does not cause corneal perforation.
Treatment. Contact lenses can be used if vision impairment is severe. If vision impairment becomes severe, corneal transplantation may be an option. In this instance, the central portion of the cornea will be replaced.
Allergy conjunctivitis
The conjunctiva, a mucous membrane that is similar to other mucous membranes in the body such as the nose or throat, is similar to those found in the nose and throat. Hypersensitivity to pollen, hay, and animals with fur is the most common cause of conjunctival allergy symptoms. People without any allergies can also experience hypersensitivity reactions at the conjunctiva level.
Symptoms. The most common symptoms of allergic reactions to the conjunctiva can be very unpleasant but are completely harmless for the eyes and vision. They can be characterized by itching, redness, and inflammation of the eye’s conjunctiva. Sometimes, there’s a lot of secretion and sticky traces. It’s often accompanied by sensitivity of light. A strong inflammation can often occur when there is a strong reaction to an environmental irritating factor.
Acute conjunctivitis
Conjunctiva secretes lubricating chemicals for the tear film. The conjunctiva also serves a defense function against infection, similar to the mucous membranes in the respiratory tract. The conjunctiva can become reddened and inflamed during a cold. This causes a sticky secretion and mucous membranes to be produced in the nose, throat, and sinuses. Although conjunctivitis can be associated with respiratory symptoms such as cold symptoms, it can also occur without them.

Symptoms. Conjunctivitis can cause burning, pain, itching, and sometimes sensitivity. Conjunctivitis can cause redness and a sticky discharge in the eyes, especially in morning.
Treatment. Virus infection is the most common cause. The symptoms usually disappear within a few days. You can wash your eyes with warm water and the symptoms will go away in no time. If the symptoms persist, it may be due to a bacterial infection. In this case, antibiotic drops are recommended. The presence of bacteria near the eyelids is suspected in cases of recurrence. You can prevent this from happening by regularly washing the eyelids with warm water and using a tissue or clean compress. It is often difficult to identify if the individual suffering from an allergy has manifestations below the conjunctiva. It is nearly impossible to determine other allergic triggers if there are no other symptoms. Eye drops can be used to treat allergic symptoms if itching is the primary symptom.
Age-related macular degeneration
The macula-lutea, which is the central part of the retina, is the only spot where vision is very clear. This area is yellow when you examine the retina. Many diseases can affect the function of photosensitive cell functions, which are concentrated in this region. Most common conditions are caused by aging. Although the causal relationship between the two is not clear, poor blood circulation and metabolic issues seem to play an important part. Lifestyle changes can only be made in rare cases to alter the course of the disease. The most common cause for vision problems in adults is age-related macular disease.
How can we identify age-related changes within the maculalutea? Most objects appear blurred or missing from the image. These problems can be easily seen while reading or performing other activities within a short radius. Perimeter, which is the area surrounding the object being observed, can be perceived clearly. Blindness is not caused by changes in the maculalutea. However, the ability to read slowly will decrease although this is usually not a rapid process. If your orientation vision decreases, it is likely that you have another condition. This should be evaluated by an optometrist.
How can age-related changes to the maculalutea be treated? There is no cure for the symptoms. Broken lines may suddenly appear when you perceive objects that are straight (e.g., a door frame, a pictureframe, etc.). This could be an indication that there is a new inflammation near the macula. An ophthalmologist should examine this. Laser treatment can sometimes be used to reduce inflammation in some cases. Laser treatment can slow down vision loss.
Photodynamic treatment. Photodynamic treatment is possible for certain types of age-related changes. Although this treatment is relatively new, it is widely available in large ophthalmology centers.
Medical Optics. Counselling is offered in the event of progressive vision loss in one or both eyes.
About posterior vitreous detachment
As we age, the vitreous body (a gel-like liquid made up of a vitreous substance) can shrink and sometimes separate from the back wall. The front portion of the eyeball may appear to have reddened areas due to small hemorhages. This shrinking is a natural result of aging. It is particularly noticeable in myopia sufferers and people who have had cataract surgery or inflammation within the eyeball. Small clots and fibers may form inside the vitreous body. This can be seen in the same manner.
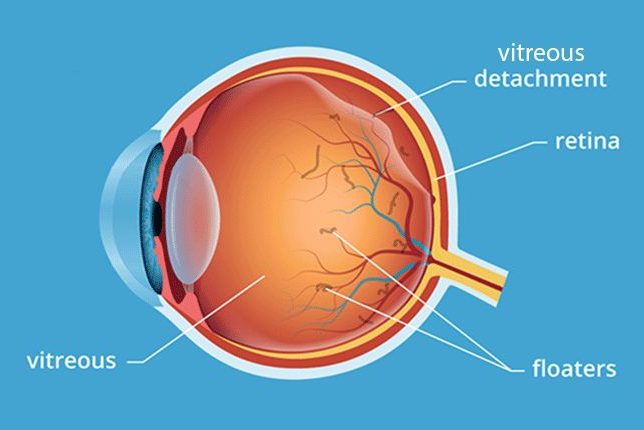
Symptoms. Affected individuals see dots, lines and circles that appear to “float” in front their eyes. The shadows that are visible on the retina from the tissue or cells affected by the disease are what is actually being seen. These shadows can be easily seen when you look at a uniform surface such as a wall or the sky.
Treatment. Treatment. A vitreous body that contracts from the posterior wall can cause damage to the retina. You should see a specialist doctor immediately if you notice more “flashes”, “spots”, or experience partial loss of vision, as well as reduced visual field. You can see these “spots” in your reading or movement of your eyes. To make the clots move, look up and down. Symptoms usually disappear with time.
Retinal detachment
When the layers of the retina are separated, it is called retina detachment. A detached retina cannot transmit visual signals to the brain. Retinal detachment, if left untreated can cause severe vision damage. Retinal detachment can be a serious eye problem that needs immediate medical attention.
Vitreous disorders (vitreous flakes)
Vitreous flakes are small spots or clouds that move around in the visual field. The majority of vitreous flakes are harmless and caused by tiny pieces of tissue within the eye. These tiny pieces of tissue can create shadows on the retina, which appear to float in your visual field when light hits them. These spots appear to be on the outer surface of the eyes, but are actually within the eye. Most cases of flakes do not cause any concern and are usually not an indication of a problem. However, an increase in flakes is a sign that something is wrong and an eye exam may be recommended.
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
Subconjunctival bleeding occurs when a blood vessel below the conjunctiva bursts and bleeds. It can happen spontaneously, as well as from vomiting, lifting weights, and coughing. It can also occur after eye surgery, or other traumas. Hypertension and diabetes are more likely to experience subconjunctival hemorhage.
Corneal infection caused by the herpes simplexvirus
Labial herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus, which can sometimes cause small skin lesions. This virus spreads via nerves in about 90% of adults. Although the mechanism behind this virus is unknown, it may be associated with minor infections or a cold. The virus is usually dormant in most people and doesn’t cause symptoms. The reason why 10% of those who are carriers have symptoms is unknown. Extreme temperatures, extreme sun exposure, emotional stress, and general health problems can all trigger the activation herpes virus.
Symptoms. Different types of corneal damage can be caused by the herpesvirus. One common lesion is the formation “branches”, which can be easily seen by an ophthalmologist using colored eye drops. The cornea is extremely sensitive to pain, and any injury to it can cause severe pain. This can be accompanied by increased lacrimal secretion, blurred vision, inflammation, and sensitivity to light. Although the infection is not contagious, it is important to practice good hand hygiene.
Treatment. Antiviral eye drops can be used to treat the inflammation. Eye drops may be used to dilate the pupil if the inflammation progresses towards the pupil. If cortisone-based drops used incorrectly, this can make the condition worse in the acute phase. Wearing an eye patch may be necessary if the sensitivity to light continues. Although an acute infection is usually treated in one to four weeks, it can sometimes take longer. The risk of permanent damage increases the deeper the infection gets into the cornea. Vision can be affected by a corneal lesion. A corneal herpesvirus infection can cause vision problems. There is a 25% chance of being infected again within the next two years. To reduce the chance of permanent damage, it is important to get treatment as soon as possible.
Viral infection of the eye
The anterior portion of the eyeball called the cornea should behave as a transparent glass with light-refracting properties. It should have a convex shape. The cornea is the most sensitive organ in the body.
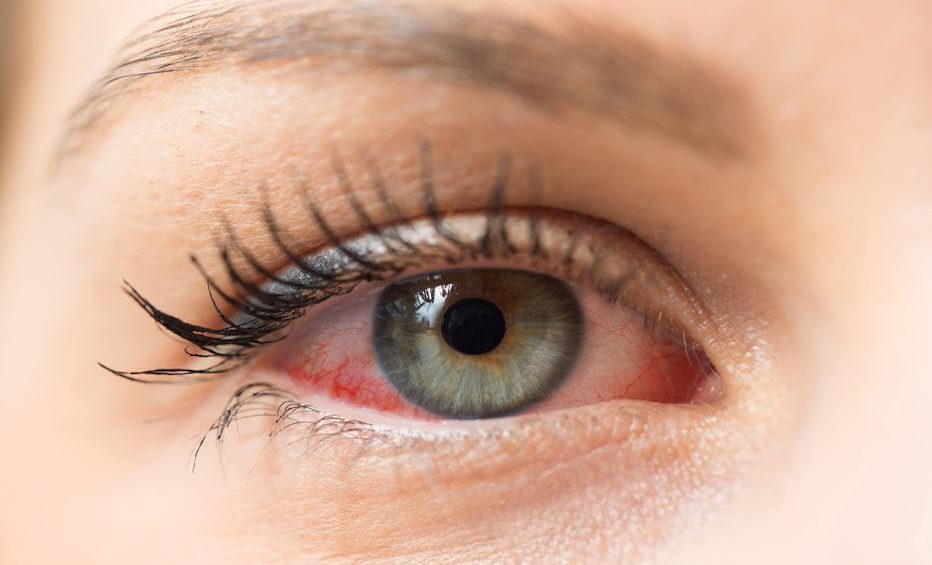
Symptoms. The appearance of small, scattered, gray spots and lesions on your cornea’s surface is often a result of viral infection. They can cause blurred vision, sensitivity to light, pain and tearing. Unwashed hands can spread the infection to others. It is important to practice good hand hygiene.
Treatment. Treatment. Sometimes, a lubricating ointment (possibly with an antibiotic ingredient) may be helpful to alleviate symptoms. The infection usually resolves on its own. However, vision can be permanently impaired in some cases. There are rare cases when healing is slow and this could indicate that the body has an overactive immune system. Cortisone eye drops can speed up the process of healing the corns. This treatment has a disadvantage: it must be continued for a prolonged period of time, sometimes even months. Sometimes temporary problems caused by contact lenses can be difficult to distinguish from viral infections. The treatment for viral infections is generally the same as for temporary problems caused by contact lenses. However, discontinuing wearing contact lenses should be considered. An infection with the herpesvirus (herpes simplex type 1) may be mistaken for a non-specific viral infection. It is recommended to use an antiherpes eye ointment if you suspect the presence of the herpesvirus. Also see Corneal infection caused by herpes simplex virus.
Inflammation or irritation of the optic nerve
It is not clear what causes inflammation of the optic nerve. It can occur without obvious external causes in many cases. Although it has been suggested that there may be some association with certain viral or inflammatory diseases, they cannot be proved.
Symptoms. The most common symptoms of inflammation of the optic nerve are a loss of vision in one eye and sometimes more. It can cause blurred vision in the central area or partial loss of central vision. The affected eye may perceive less saturated colors than the healthy one.
Treatment. Most cases of inflammation disappear within a few weeks. Cortisone tablets have not been shown to be effective in treating inflammation. It is impossible to stop the progression of the disease by changing your lifestyle. However, it is important to avoid alcohol and other substances which can cause damage to the nervous system. The cure is generally complete and leaves no visible symptoms. The risk of developing other inflammatory episodes is decreased if there are no other medical conditions. Recurrent episodes can cause damage to the optic nerve which could lead to vision loss.
Pinguecula
Pinguecula refers to a small yellowish-yellow spot that appears on the conjunctiva. It is usually located on one side of the cornea. Pinguecula can be caused by ultraviolet radiation, wind, or dust. It is most common in people who spend a lot of time outside, especially in bright environments.
Pterygium
A pterygium refers to an abnormal, wedge-shaped growth that forms on the cornea. The conjunctiva’s abnormal growth on the cornea causes this raised growth. It is not cancer. It isn’t clear what caused pterygium to appear. Their development is likely to be due to long-term sun exposure and chronic irritation by drought conditions. People who live in tropical areas are more likely to develop pterygium.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that can affect anyone with diabetes. There are usually no or very few visual symptoms in the early stages. Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that can permanently damage the retina if not treated promptly. This condition can lead to vision problems if not treated early. These symptoms include blurred vision in the near and far, flakes, and sudden vision loss. It can lead to blindness or severe vision loss if it is not treated. Ophthalmic surgeons can’t repair the damage done by diabetic retinalopathy. However, modern treatment methods can slow down the disease progression and even prevent it from becoming severe. Patients with diabetes should be checked regularly even if they don’t have any symptoms. Patients with diabetes should immediately see their doctor if they notice any changes in their vision.
Find XNXX, XXNXX, XXNX porn for arab hd and 4k https://xnxxyouporn.com/57451/, https://xnxxyouporn.com/65902/, https://xnxxyouporn.com/59576/, https://xnxxyouporn.com/60527/, https://xnxxyouporn.com/60631/,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  .
.
Scleritis, episcleritis
Scleritis is the medical term for inflammation of sclera. If the inflammation is superficial, we call it “episcleritis”, which can be more serious and common. It is not known what causes inflammation of the skin. These conditions may be linked to rheumatism or connective tissue disorders, particularly in the case of deep scleritis. Although episcleritis can occur in many cases, it is often associated with these conditions. However, it may also be associated with other conditions such as infections and hormonal changes.
Symptoms. Episcleritis causes reddening in the eyes, but only in a small area. Sometimes, the reddening can be severe and may take on a bluish tint. The reddening area can become sensitive to pain and may be accompanied by various levels of pain. Scleritis symptoms are similar to scleritis, but the reddening affects a larger area.
Treatment. Treatment. Anti-inflammatory eye drops, which are usually based on cortisone, can be effective in many cases. Healing takes between 1-2 weeks and even longer. Scleritis can be treated in conjunction with any other rheumatic conditions or connective tissue disorders. Scleritis is one condition that can recur, but not always. It is difficult to predict the possibility of new inflammations in every case. The greater your chances of healing, the sooner you start treatment.
Orjelet (The Jug).
When one of the glands on the edge of your eyelid becomes infected, a stye will develop. A stye is similar to a pimple. It can grow either inside or outside of the eyelid. Pitchers can appear at any age. It causes reddening and swelling in the affected areas. It does not usually block the view.



